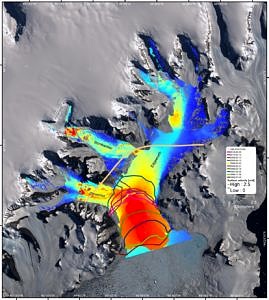
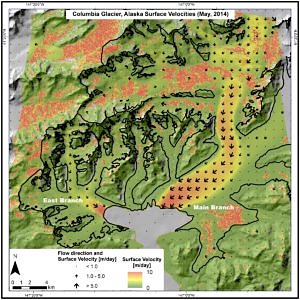
AG Fernerkundung-GIS (Braun)
 Our research focuses on aerial and satellite image analysis as well as geographic information systems. We use time series of optical earth observation systems in various spatial and spectral resolutions, from synthetic aperture radar systems(SAR) as well as other imaging and non-imaging sensors in combination with field measurements.
Our research focuses on aerial and satellite image analysis as well as geographic information systems. We use time series of optical earth observation systems in various spatial and spectral resolutions, from synthetic aperture radar systems(SAR) as well as other imaging and non-imaging sensors in combination with field measurements.
Our applications are in the field of glaciology and the effects of climate change on the cryosphere, including changes in ice dynamics, glacier mass balance and contributions to sea level or properties of snow and ice. Analyzes of land use and land cover change are also components of our work, such as applications in the field of nature conservation management, biodiversity research or studies on ecosystem functions.
Katrina Lutz
- E-Mail: katrina.lutz@fau.de
Philipp Malz
- E-Mail: philipp.malz@fau.de
Akash Patil
- E-Mail: akash.patil@fau.de
Dakota Pyles, M.Sc.
- E-Mail: dak.pyles@fau.de
Project staff: Thorsten Seehaus (PI), Diego Pacheco Ferrada
Glaciers and ice caps outside the polar ice sheets are strongly affected by climate change, and
various observables are defined as essential climate variables. Glacier shrinkage has local to
regional-scale impacts on hydrology, ecosystems, and society. In the Tropical Andes, the
glaciers pose an important water resource and significantly contribute to the local and regional
water supply, especially during the dry season and drought periods. Moreover, glacier retreat
increases the risk of glacier lake outburst floods putting downstream communities at risk. To
improve future water management and risk assessment as well as to evaluate the impact of
climate variations, region-wide and detailed information on the past, present, and future glacier
evolution in the Tropical Andes is required. Current glacier mass change estimates have
spatiotemporal limitations and often considerable uncertainties, while regional projections,
carried out within global analyses, show partly ambiguous trends.
This project aims to overcome these deficiencies by comprehensively analyzing the Tropical
Andes‘ past, present, and future glacier evolution. An improved regional assessment of current
and future glacier changes will be conducted based on an innovative combination of multi-
mission remote sensing data, in-situ measurements, and glacier and hydrological modeling. In
combination with data on past glacier changes, which are obtained by exploiting unique remote
sensing archives, the evaluation of the long-term trend and its relation with climate change will
be facilitated. By assimilating the new remote sensing products and in-situ observations into an
ice-dynamic model inversion, highly improved ice volume distribution information will be
generated. Projections of glacier evolution for the Tropical Andes until 2100 using mass balance
modeling, optimized for the tropics, and fully 3-dimensional glacier modeling will be conducted
to overcome the shortcomings of existing global estimates. Those activities will facilitate the
subsequent study of the glacier lakes evolution and the glacier meltwater contribution to
catchment runoff.
The outcomes of this project will include novel and improved regional information regarding the
glacier evolution in the Tropical Andes and methodological advances. These comprise (1)
region-wide enhanced quantification of the ongoing glacier changes, the evaluation of its long-
term trend and correlation with climatic variations, (2) development of innovative remote sensing
and modeling techniques, (3) improved ice thickness information and projections of glacier and
runoff evolution using fully coupled, 3D-distributed, and optimized modeling.

Funded within the Emmy Noether Programme of the German Research Foundation (DFG)
International Doctoral Programme: Measuring and Modelling Mountian Glaciers in a Changing Climate (IDP M³OCCA)
Lead: Franzika Temme (Coordination), Johannes Fürst, Illaria Tabone, Matthias Braun (Speacker), Thorsten Seehaus
Improve current mass change estimates of glaciers by innovatve technologies, develop new and improve existing algorithms for variable retrieval by deep learning. In addition, we aim at assimilating and linking various geophysical models and improve their performance by machine learning techniques. For more information on IDP M³OCCA please visit the project website.
In cooperation with FAU (Informatics, Mathematics, Electrical Engineering), Bavarian Academy of Sciences, DLR Microwave Radar Institute in Oberpfaffenhofen and Technical University of Munich
Funding period 2022-2025
Funded within the Elite Network Bavaria by the Bavarian State Ministry of Science and the Arts
Climate sensitivity of western Antarctic Peninsula ice shelves (CSAPIS)
Project staff: Matthias Braun, Antonia Warnstedt, Martin Rückamp
Funding period 2022-2025
Funded within the DFG Priority Programme Antarctic Research SPP1158
Unlocking the glaciological information of historical aerial imagery to obtain long-term glacier mass balance information and to identify drivers of glacier changes on the Antarctic Peninsula (UNLOC)
Project staff: Thorsten Seehaus, Vijaya Kumar Thota
The Antarctic Peninsula is a hot spot of global warming and leading to considerable changes in its ice sheet and outlet glaciers. Pronounced glacier recession has been reported since the 1950s throughout the Antarctic Peninsula and many of its ice shelves disintegrated or significantly retreated within the last decades. Consequently, the ice masses of the Antarctic Peninsula contribute significantly to global sea-level rise. However, estimates of the mass budget of the Antarctic Peninsula are subjected to considerable uncertainties due to various issues. Moreover, long-term information on the evolution of the mass balances exists only for a very limited amount of glaciers.Since the 1950s, various aerial campaigns were carried out to map the Antarctic Peninsula. The acquired photogrammetric imagery poses a “time capsule” of information on the historic glacier states. Thus, we aim within this project to unlock this information from the historic aerial imagery by applying state-of-the-art photogrammetric analysis techniques to reconstruct the former glacier surface elevations. The analysis will be supported by providing precise ground control points, which will be acquired during a joint aerial survey with AWI and DLR in late 2022. By combining the information revealed from the historic imagery with recent surface elevation information from the German bistatic SAR mission TanDEM-X, the computation of long-term glacier volume and mass changes on the Antarctic Peninsula will be facilitated. Finally, all available information on glacier changes will be correlated with oceanic, atmospheric, and glacier geometry parameters in order to identify driving factors of the revealed glacier variations. This information will facilitate a better understanding of the ongoing processes and interaction between the different spheres, and will be highly beneficial for projections of glacier evolution on the AP Ice Sheet and future sea-level rise contribution.
Funding period 2023-2026
Funded within the DFG Priority Programme Antarctic Research SPP1158
Large-scale Automatic Calving Front Segmentation and Frontal Ablation Analysis of Arctic Glaciers using Synthetic-Aperture Radar Image Sequences (LASSI)
Project staff: Thorsten Seehaus, Vincent Christlein, Daktoa Pyles, Marcel Dreier
The arctic glaciers are strongly affected by global climate change, in particular due to the Arctic amplification phenomenon. Thus, they contribute significantly to current sea level rise. There exists only sparse information on glacier front variations as well as the evolution of frontal ablation and its drivers for the huge amount of tide water glaciers in the Arctic. However, the steadily increasing amount of available remote sensing data, in particular since the launch of the Sentinel satellites within the Copernicus Program by ESA and the European Commission, facilitates large-scale spatio-temporal monitoring of glacier changes. Within the proposed project, we aim at applying deep learning techniques to automatically map calving front positions of arctic tidewater glaciers, by means of Sentinel-1 SAR imagery. Therefore, we will implement and evaluate different deep learning segmentation models, including also time-series information from SAR image sequences. To improve the robustness and performance of our segmentation results, we will enlarge the field-of-view by incorporating attention mechanisms, apply multi-task learning, and fine-tune our best model in a semi-supervised manner on glaciers not yet included in the training database. Uncertainty bounds will increase the interpretability of our model’s results. For the best performing approach, a fully automated operational processing pipeline will be implemented and applied on the huge amount of available Sentinel-1 imagery throughout the Arctic. Subsequently, the obtained information on glacier front changes will be combined with information on ice flux at the termini and climatic mass balance data to estimate frontal ablation. By including information on total mass balances of the glaciers and climatic mass balance data from regional climate modeling or down-scaling of reanalysis data, the contribution of frontal and surface mass balances to the total mass balance will be estimated. Finally, the obtained results on glacier changes in combination with information on atmospheric, oceanic, sea ice, and glacier geometry parameters will be analyzed using multivariate statistical approaches to identify the drivers of the observed glacier changes. The project results will enhance our understanding of the ongoing processes and cross-links between the different spheres. Moreover, we will obtain fundamental reference data for numerical glacier modeling, subsequently leading to improved projections of glacier evolution and sea-level changes.
Funding period 2022-2025
Funded within the DFG Priority Programme Antarctic Research SPP1158
Polar-5 geodetic & geophysical airborne surveys on the Antarctic Peninsula (INSULATE & APGCP)
Project staff: Thorsten Seehaus, Matthias Braun
The aim of this airborne survey is to acquire high-resolution aerial photography on the south-central Antarctic peninsula using the high-resolution Polar-MACS camera system. In addition, laser scanning and radio echo sounding will be carried out on Wordie Ice Shelf tributary glaciers.
In cooperation with AWI Bremerhaven and DLR Adlershof
Funding period 2021 & 2022 (postponed to 2023 &2024)
Polar-5 geodetic & geophysical airborne surveys in Fuego-Patagonia (PataFuego 2021 & 2022)
Project staff: Moritz Koch, Matthias Braun, Johannes Fürst
The activity aims at acquiring various glaciological variables over the icefield and glaciers of Patagonia and Tierra del Fuego. The Polar-5 aircraft is operated out of Puerto Natales, Chile. We acquire data with various sensor systems like laser scanner, a long-range laser altimeter, high-resolution aerial photography, accumulation radar and various meteorological instruments. We repeat tracks of previous measurements by other groups in order to allow precise elevation change measurements. The data also serves as reference for spaceborne elevation change measurements from the german TanDEM-X mission.
In cooperation with AWI Bremerhaven, TU Dresden and TU Darmstadt as well as various partners from South America
Funding period 2021 & 2022
Ice thickness, remote sensing and sensitivity experiments using ice-flow modelling for
major outlet glaciers of the Southern Patagonian Icefield (ITERATE)
Project staff: Moritz Koch, Matthias Braun, Johannes Fürst
The project aims at improving our process understanding of glacier changes and their constraints and sensitivities to potential future perturbations. In order to achieve those goals we will acquire new data, update our existing comprehensive spatial databases and combine information into local-scale ice-flow modelling and an analysis of different forcing scenarios. Specifically we will acquire additional ice thickness data using helicopter-based ice penetrating radar surveys as well as airborne laser scanning surveys. The airborne surveys are carried our in close cooperation our international partners. We will temporally densify our spatial information on glacier extent from optical satellite data, compute surface velocity fields by intensity offset tracking from regular Sentinel-1 radar imagery and compute improved surface elevation and mass change estimates. We will assimilate our spatial fields in a state-of-the-art ice thickness reconstruction approach. Latter will be constraint by the new and existing ice thickness measurements from different groups as well as by novel bathymetric data in order to generate a new map of the bedrock topography. We will adapt our existing reconstruction approach since we will have to weight the different ice thickness measurements in regard to their quality. The last task comprises the setup of high-resolution ice dynamic models for specific glaciers, namely Perito Moreno, Upsala and Viedma glaciers. We will specifically test different calving routines implemented in ELMER/Ice and perform perturbation experiments in order to test the glaciers’ sensitivity on certain variables and parameters like bed elevation, basal friction, lake level, calving parameters and frontal ablation.
Funding period 2021-2024
Mass balance and ice dynamics of Antarctic Peninsula glaciers (MIT-AP)
Project staff: Thorsten Seehaus
Pronounced climatic changes have been observed at the Antarctic Peninsula within the past decades and its glaciers and ice caps have been identified as a significant contributor to global sea level rise. Dynamic thinning and speed-up was reported for various tidewater glaciers on the western Antarctic Peninsula. On the east coast, several ice shelves disintegrated since 1995. Consequently, former tributary glaciers showed increased flow velocities due to the missing buttressing, leading to substantial ice mass loss. Various studies were carried out to quantify the ice mass loss and ice discharge to the ocean at the Antarctic Peninsula using different approaches. However, the results are still subject to substantial uncertainties, in particular for the northern section of the Antarctic Peninsula (<70°S).
Thus, the aim of this project is to carry out an enhanced analysis of glacier mass balances and ice dynamics throughout the Antarctic Peninsula (<70°S) using various remote sensing data, in-situ measurements and model output. By analyzing bistatic SAR satellite acquisitions, an unprecedented spatial coverage with surface elevation change information at the study area will be achieved to compute multi-temporal geodetic glacier mass balances on regional and glacier scales. Information on ice dynamics will be derived from multi-mission SAR acquisitions using offset tracking techniques. In combination with latest ice thickness data sets the spatiotemporal variability of the ice discharge to the ocean will be evaluated. By including information from in-situ measurements and model output of atmospheric and oceanic parameters, driving factors of the obtained change patterns will be assessed to enhance the understanding of the ongoing change processes.
The project results will contribute fundamental information to international initiatives and institutions like IMBIE, IPCC and WGMS and address several “Advancing Earth System Science Challenges of the Living Planet”, defined by ESA.
Funding period 2020-2022
SATELLITE – A stochastic eStimATe of sEa Level contribution from gLaciers and Ice caps using satellite remoTe sEnsing
Project staff: Christian Sommer, Philipp Malz, , Matthias Braun
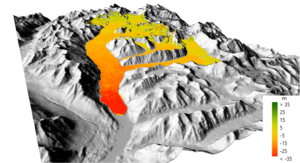
The project aims at deriving a stochastic global sampling for ice volume and mass loss of glaciers and ice caps based on repeat satellite observations. For this purpose we will develop a respective sampling strategy. We propose two observation intervals: a period 2000-2012 between 56°S and 60°N and a second interval covering 2012 to 2014 or later (globally) in order to quantify potential changes in ice volume/mass loss rates.
Geodetic glacier-specific mass balances will enable us to quantitatively compare changes and change rates in different regions of the world using the same methodology. We base our analysis on data from the German satellite mission TanDEM-X and integrate it with observations and data products from other sources (like SRTM, ASTER, Landsat, ICESat-1/2, WGMS records, field and airborne measurements). The German TanDEM-X satellite mission operated since 2010 provides a unique database with its bi-static satellite configuration.
Funding period : 2016-2019
Website: www.spp-sealevel.de
FRAGILE – Next generation framework for global glacier forecasting
Worldwide glacier retreat outside the two large ice sheets is increasingly tangible and the associated ice-loss has dominated the cryospheric contribution to sea-level change for many decades. 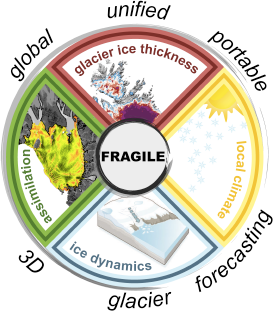 This retreat has also become symbolic for the effects of the generally warming climate. Despite the anticipated importance for future sea-level rise, continuing glacier retreat will affect seasonal freshwater availability and might add to regional water-stress in this century. Here, I envision a novel self-consistent, ice-dynamic forecasting framework for global glacier evolution that will lift the confidence in forward projections for this century to new heights. For the first time, each glacier on Earth will be treated as a three-dimension body within its surrounding topography without using any form of geometric simplification. The heart of the framework is the systematic utilisation of the rapidly growing body of information from satellite remote sensing. For this purpose, I intend to pass on to ensemble assimilation techniques that transiently consider measurements as they become available. This will streamline and increase the total information flow into glacier models. In terms of climatic forcing, global products will be replaced by regional forecasts with high-resolution climate models. Moreover, a more realistic representation of the local energy balance at the glacier surface is pursued that ensures multi-decadal stability in the melt formulation. The envisaged 3D finite-element modelling framework also allows a direct integration of iceberg calving, which is, on global scales, an oftenunconsidered dynamic ice-loss term. To this day, a key limitation of glacier projections is the poorly constrained ice volume and its distribution at present. Here, I put forward a promising remedy that builds on multi-temporal satellite information to calibrate a state-of-the-art reconstruction approach for mapping basinwide ice thickness on virtually any glacier.
This retreat has also become symbolic for the effects of the generally warming climate. Despite the anticipated importance for future sea-level rise, continuing glacier retreat will affect seasonal freshwater availability and might add to regional water-stress in this century. Here, I envision a novel self-consistent, ice-dynamic forecasting framework for global glacier evolution that will lift the confidence in forward projections for this century to new heights. For the first time, each glacier on Earth will be treated as a three-dimension body within its surrounding topography without using any form of geometric simplification. The heart of the framework is the systematic utilisation of the rapidly growing body of information from satellite remote sensing. For this purpose, I intend to pass on to ensemble assimilation techniques that transiently consider measurements as they become available. This will streamline and increase the total information flow into glacier models. In terms of climatic forcing, global products will be replaced by regional forecasts with high-resolution climate models. Moreover, a more realistic representation of the local energy balance at the glacier surface is pursued that ensures multi-decadal stability in the melt formulation. The envisaged 3D finite-element modelling framework also allows a direct integration of iceberg calving, which is, on global scales, an oftenunconsidered dynamic ice-loss term. To this day, a key limitation of glacier projections is the poorly constrained ice volume and its distribution at present. Here, I put forward a promising remedy that builds on multi-temporal satellite information to calibrate a state-of-the-art reconstruction approach for mapping basinwide ice thickness on virtually any glacier.
European Research Council (ERC) – Starting Grant
Period: 2021 – 2026
Project staff: Theresa Diener, Johannes Fürst
GROCE (TP 7): Supra-glacial melt water at the 79° Glacier, Greenland
Project staff: Katrina Bartek, Matthias Braun
The subproject will detect supra-glacial meltwater ponds in its spatial and temporal variation. Hereto, data of various national and European SAR systems, like TerraSAR-X and TandDEM-X, COSMO-Skymed, Sentinel-1 as well as optical data from the Sentinel-2 mission will be used. To map the melt dynamics and the supra-glacial lakes we develop novel algorithms based on deep learning. We will also estimate the depth and volume of the meltwater ponds combining field observations and data from the NASA ICESat-2 spaceborne laser altimeter.
Project partners:
Laufzeit: 2017 – 2020, 2020-2023
Web site: www.groce.de
Funded by 
MAGIC – The Mountain Glacier Forecast Framework
General glacier retreat around the globe has become iconic to illustrate the effects of global warming and we anticipate that this demise will continue and significantly add to global sea-level rise. Ice loss can also induce shifts in regional water resources, putting some places at high risk of year-around freshwater availability. Better projections of glacier retreat are therefore essential in terms of coastal impact, water management and hydro-glaciological risks. The overall aim of the project is to provide a framework to improve past and future glacier volume projections. The process-based framework will be based on the open-source ice-flow model Elmer/Ice and will allow to reduce three potentially important sources of uncertainty. Anticipating the continuously growing body of information from satellite remote sensing, we will improve and develop robust data assimilation methods to infer the basal topography beneath the ice and calibrate ice-flow parameters for a better representation of the initial state and ice dynamics. The flow model will be coupled to an enhanced surface mass balance model that exhibits a stable melt relation over relevant multi-decadal timescales. Based on ensemble simulations, the framework will allow to better quantify the interaction and propagation of these uncertainties. As a proof of concept, the framework will be applied to hindcast and forecast glacier evolutions in the French Alps and in Cordillera Darwin (Chile). These sites have been chosen because for both glacier sites ice-flow is considered important and because of the availability of in-situ and remotely sensed observations. The two sites will further serve as challenging test setups to scrutinise the applicability, performance and robustness of the modelling framework under different climatic conditions and dynamic settings.
Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) – Project ID: 431767937![]()
Period: 2020-2023
Project staff: Franziska Temme, Johannes Fürst, Fabien Gillet-Chaulet
STRG – Surface state of Tropical Glaciers – Polar 5 aerial survey
- Precise topographic information of the pronounced topography of topical
glaciers is lacking, leading to limitations in ice modelling and mass balance
computations - Glacier albedo is affected by the deposition of black carbon (e.g. due to bio mass burning
in the Amazon) on the glacier surface, leading to increased ice melt. - Within the proposed flight campaign, high-resolution multispectral photogrammetric
imagery will be acquired in order to obtain topographic, spectral, albedo, and thermal
Information on the glacier surfaces.
Period: 2024-2025
Project staff: Thorsten Seehaus
Detection of birds and marine mammals in aerial image sequences using artificial intelligence methods (EVERLASTING)
Project staff: Christian Sommer, Mathias Seuret, Matthias Braun, Vincent Christlein
As a result of the current expansion of offshore facilities for the generation of renewable energy and shipping traffic, the assessment of impacts on marine ecosystems is becoming increasingly important. Precise knowledge of the spatial and temporal distribution of animal species is therefore essential for the conservation of biodiversity and the management of offshore wind farms and other economic activities. High-resolution optical images from the latest generation of airborne remote sensing sensors enable the observation of seabirds and marine mammals in large marine areas. However, identifying features on the ocean surface and separating animals from other objects such as wave structures, ships or buoys requires time-consuming visual inspection of the acquired image sequences by trained personnel. To overcome this limitation of previous assessments, the EVERLASTING project is a joint effort of the FAU Institute of Geography and the Pattern Recognition Lab (LME) to develop an AI-based approach to automatically detect and classify various features above the sea surface. As training data, we use an extensive database of optical images (~2.5 million images) with a spatial resolution of 2 cm, acquired by the German Federal Agency for Nature Conservation (BfN) during repeated monitoring flights in the German North Sea and Baltic Sea since 2018. These images are then pre-processed and geolocated with the respective supporting information to create a comprehensive test dataset of marine animal observations. Manual annotations (image labels) of features detected during visual inspection are available for a fraction of the total survey database and serve as AI training data. The AI method we are developing must be capable of both detecting birds in images and tracking instances of the same element in multiple images. Challenges include image quality (i.e. contrast & brightness), feature size and motion. Often features (birds) appear in several successive overlapping images, making it difficult to estimate the number of animals detected. We aim to address these issues by incorporating cinematic estimation of the movement of the aircraft and animal, as well as estimation of the direction of the sun in each frame, into the tracking system. The outcomes of the project will be used by the German Federal Agency for Nature Conservation (BfN) to expand the monitoring of seabird and mammal populations and to evaluate the effectiveness of biodiversity conservation measures.
Period: 2023-2026
Funded by 
Completed Projects
EU BiodivERsA, DFG FE 1331/3-1
Funding period: 2014-2017
Project team: Hannes Feilhauer, Sandra Skowronek

Biodiversity conservation includes the development of warning and rapid response systems for biological invasions and urges investigations of their impacts on ecosystem function and services. In this context, the systematic, objective, and synoptic view on Earth of remote sensing systems offers a great opportunity to target biological invasion and their impact across various spatial and temporal scales. Within DIARS we aim to
1. characterize the ecosystem impact of invasive plant species through the combined use of field and remotely sensed data.
2. support monitoring, prediction of spread and risk assessment of invasive plant species as preconditions for management measures and mitigation.
For this purpose, we analyse and map the local distribution of the invasive species Campylopus introflexus, Prunus serotina and Oxalis pes-caprae and their impact on ecosystems in Germany and France.
Project website: DIARS
Project partners:
- Carnegie Department of Global Ecology, Stanford, CA, USA
- Fondazione Edmund Mach, San Michele all’Adige, Italy
- KIT, Karlsruhe, Germany
- KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium
- U de Picardie Jules Vernes, Amiens, France
- Vito, Mol, Belgium
DFG FE 1331/2-1
Funding period: 2013-2014
Project team: Hannes Feilhauer

Maps of vegetation patterns such as spatial variation in floristic composition, plant traits and plant functional types are required in ecology, ecosystem modelling and nature conservation. One frequently applied approach to generate these maps relies on imaging spectroscopy. In this approach, statistical relationships between a vegetation sample and the corresponding canopy reflectance are quantified and subsequently applied onto the imagery.
Although several successful examples of such applications exist, fundamental questions regarding the causal relations between vegetation patterns and canopy reflectance are still open. In particular the role of canopy optical traits remains poorly understood. Canopy optical traits determine the reflectance signal of vegetation and include canopy biochemistry, morphological and structural properties. CaTReS aims to test the qualitative and quantitative contribution of these traits to remote sensing of vegetation patterns in a test site in Southern Bavaria.
DFG-Priority Programme 1158 Antarctic Research
BR2105/8-1
Funding period: 2009-2014 (completed)
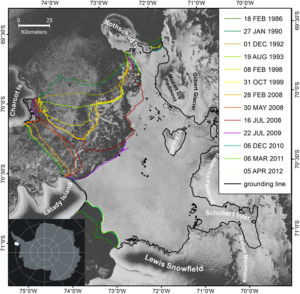 This project aims to gain understanding of ongoing and potential changes of Wilkins and GeorgeVI ice shelves on the south-western Antarctic Peninsula. Both are located in an area of the supposed climatic limit of viability of ice shelves and have already shown considerable ice front retreat. The break-up events in 2008 and 2009 on Wilkins Ice Shelf exemplified their potential of disintegration.
This project aims to gain understanding of ongoing and potential changes of Wilkins and GeorgeVI ice shelves on the south-western Antarctic Peninsula. Both are located in an area of the supposed climatic limit of viability of ice shelves and have already shown considerable ice front retreat. The break-up events in 2008 and 2009 on Wilkins Ice Shelf exemplified their potential of disintegration.
Within a multi-institutional, interdisciplinary approach including remote sensing (FAU Erlangen-Nürnberg), modeling of the ice dynamics (Alfred-Wegener-Institut) and fracture mechanics (TU Kaiserslautern), we aim to improve the understanding of the impacts of temperature increase on ice shelf stability.
The remote sensing component includes the mapping of surface structures and fracture development over time, as well as the derivation of surface velocity fields by SAR interferometry and feature tracking for the Wilkins Ice Shelf, which are required as input datasets for modeling of fracture and ice dynamics. For this purpose, we use multi-temporal optical and SAR imagery (Alos Palsar, TerraSAR-X, ERS, ENVISAT). Further work tasks include the investigation of ice thickness changes based on altimetry data and the mapping of the grounding line using Differential SAR Interferometry. The observed quantities are interpreted in the context of ice dynamics and fracture mechanics.
Project team
BayIntAn – Reconstruction of climate at Glaciar Perito Moreno
Funding period: 2014
Klimarekonstruktion am Perito Moreno Gletscher in Patagonien auf Basis von dendro-ökologischen Untersuchungen, meteorologischen Messungen und Fernerkundung
Die Messung verschiedener dendroökologischer Parameter wie Jahrringbreiten, Holzdichte und die Analyse der zeitlichen Variabilität der stabilen Isotope ermöglicht es Rückschlüsse auf vergangene Klimabedingungen zu ziehen, bevor irgendwelche Klimamessungen in der Region gemacht wurden (wir erwarten Aufzeichnungslängen von etwa 200 Jahren). Die dendrochronologischen Zeitreihen werden mit meteorologischen Daten einer automatischen Wetterstation am Südrand des Glaciar Perito Moreno kalibriert, die seit fast zwei Jahrzehnten kontinuierlich aufzeichnet. Dies ermöglicht es, eine Beziehung zwischen den in Baumringen gespeicherten Umweltvariablen und dem lokalen Klima herzustellen. Das ermittelte Klimasignal wird mit dem Gletscherverhalten und der Sensibilität des Gletschers gegenüber klimatischen Veränderungen verknüpft.
Der Perito Moreno ist der einzige Gletscher im Nationalpark Los Glaciares mit fast 2 Jahrzehnten ununterbrochenen meteorologischen Messdaten und einer einzigartigen Lage, um die Jahrringmessungen mit in-situ meteorologischen Beobachtungen zu kalibrieren. Die Baumarten der Gattung Nothofagus oberhalb der rezenten Lateralmoräne garantieren eine sehr starke Verbindung zwischen lokalem Klima und den Baumring Informationen sowie eine lange zeitliche Aufzeichnung. Anschließend an den Standort am Perito Moreno wird entlang des klimatischen Transekts, von feuchteren in trockenere Bedingungen, beprobt – die Standorte innerhalb des Nationalparks repräsentieren feuchte Bedingungen, während die Standorte außerhalb des Parks (nach Osten) trockenere Bedingungen aufweisen.
In Kooperation mit Pedro Skvarca, Glaciarium, El Calafate, Argentinien).
Anschubfinanzierung des Bayerischen Förderprogramms zur Anbahnung internationaler Forschungskooperationen (BayIntAn), 2014.
Gefördert durch:
BAYLAT (Bayerische Hochschulzentrum für Lateinamerika)
BayFor (Bayerische Forschungsallianz)
BayIntAn (Bayerisches Förderprogramm zur Anbahnung internationaler Forschungskooperationen)
Projektbeteiligte/ Project team
Björn Saß, Jussi Grießinger, Matthias Braun
EU FP7 IRSES
Funding period 2012-2016
IMCONet is an international Research Network that follows an interdisciplinary approach to understand the consequences of Climate Change in coastal Western Antarctica. A Network for Staff Exchange and Training, IMCONet is funded by the Marie Curie Action IRSES (International Research Staff Exchange Scheme) of the 7th Framework Programme of the European Union. The activity brings European, South American and US scientists together to advance climate and (eco-) system change research at the Western Antarctic Peninsula (WAP), a region of recent rapid aerial warming.
IMCONet objectives are
- to develop predictive climate change and ecosystem models for the whole WAP coastal environment based on existing data sets and data exchange policies;
- transfer of knowledge between partner countries to enhance collaboration with high quality long-term measuring programs at all 3 stations, to fill present measuring gaps.
IMCONet is the follow-up of the ESF PolarCLIMATE activity IMCOAST, an international research activity that investigated climate change and glacier melting effects on coastal ecosystems at Potter Cove and in Admiralty Bay on King-George Island (Isla 25 de Mayo) in the northern WAP region. Data were generated for different ecosystem compartments (glaciers, coastal run-off and sediment biogeochemistry, pelagic and benthic coastal systems) by interdisciplinary multi-national teams collaborating mainly on-site.
The consortium is coordinated by AWI Bremerhaven; within the project FAU coordinates the WP1 on glacier mass balance.
Project team:
Matthias Braun (FAU), Thorsten Seehaus (FAU), Juliana Costi (FURG/FAU), Ulrike Falk (Uni BN), Jorge Arigony-Neto (FURG), Hernan Sala (IAA), Sebastian Marinsek (IAA), Adrian Silva Busso (IAA)
DFG-Priority Programme 1158 Antarctic Research
BR 2105/9-1
Funding period: 2012-2015
Climate conditions along the Antarctic Peninsula have considerably changed in the last 50 years. The glaciers on the Western Antarctic Peninsula have already shown reactions of change by speed-up and surface lowering. The disintegration of the Larsen-A and B Ice Shelves, the ice shelves in the Larsen Inlet, Prinz-Gustav-Channel and Wordie Ice Shelf have led to a surge-type behaviour of tributary glaciers to which much of the current contribution of Antarctic Peninsula ice to sea level rise is attributed. However, quantifications of mass loss from the peninsula using different observations and methods are still ambiguous.
The aim of our project is on to improve the quantifications of mass loss in the area of the former Northern Larsen-A embayment as well as for Western Antarctic Peninsula glaciers. In order to achieve those goals we analyse time series of satellite data from ERS 1/2, Envisat, Radarsat 1, ALOS PALSAR, TanDEM-X & TerraSAR-X and Rapideye to determine glacier velocity changes for these regions over the last 20 years. Furthermore we generate digital elevation models from TanDEM-X mission data in order to calculate surface elevation changes. Our products are backed up with GNSS ground truth measurements from joint German-Argentine (DNA_IAA) field campaigns and laser altimetry done by collaborating partners (Alfred Wegener Institut, Bremerhaven). In an integrated analysis those data sets are linked to achieve a better glaciological understanding of underlying processes and to estimate the ice mass loss at the study region.
Project team
Gletschermonitoring in Hochasien mittels TanDEM-X InSAR und weiterer Erdbeoachtungssensorik
Projektteam: Matthias Braun, Melanie Rankl, Philipp Malz
Projektlaufzeit: 2015-2017
Übergeordnetes Projektziel ist eine Eignungsanalyse von Daten der TanDEM-X Science Phase sowie die Entwicklung einer Prozessierungskette zur Ableitung geodätischer Massenbilanzen. Zudem sollen Änderungen der Dynamik und Ausdehnung der Gletscher Hochasiens auf verschiedenen zeitlichen und räumlichen Skalen erfasst werden. Das zu entwickelnde Produkt ist ein validiertes „Methodeninstrumentarium zur Gletscherbeobachtung“, das nicht nur in Hochasien, sondern auch in anderen Gebirgsregionen zur Beobachtung der dem globalen Klimawandel unterliegenden Gletscher eingesetzt werden kann. Die Innovation liegt in der Bewertung des Potenzials der experimentellen Aufnahmemodi der TanDEM-X Science Phase für die glaziologische Fernerkundung in Bezug zur bisherigen Aufnahmekonfiguration sowie in der Kombination mit glaziologischen Produkten basierend auf Daten verschiedenster Satellitenmissionen. Das interferometrische Potenzial der Mission und dessen Eignung für steile Hochgebirgstopographien soll systematisch analysiert und Empfehlungen für die weitere Missionsplanung gegeben werden. Am Projektende soll eine verbesserte regionale Aussage zu den Massenänderungen der Gletscher in Hochasien stehen, die z.B. in internationale Berichte wie den IPCC AR6 einfließen kann.
Projektpartner: Prof. Dr. Volker Hochschild, Eberhard-Karls Universität Tübingen
gefördert durch:
HGF Alliance
Funding period: 2012-2017
The HGF Alliance “Remote Sensing and Earth System Dynamics” (EDA) aims at the development and evaluation of novel bio/geo-physical information products derived from data acquired by a new generation of remote sensing satellites; and their integration in Earth system models for improving understanding and modelling ability of global environmental processes and ecosystem change.
The key objective of the proposed Alliance is to prepare the HGF centers and the national/international science community for the utilisation and integration of bio/geo-physical products provided by the next generation radar remote sensing missions (e.g. Tandem-L) into the study of natural and anthropogenic impact on Earth’s ecosystems by:
-
developing new bio/geo-physical information products from remote sensing data;
-
integrating the new products into Earth system models;
-
improving the understanding and modelling of dynamic processes;
-
providing a unique forum for the education of a new generation of scientists.
Our working group forms part of the cryosphere workpackage of the HGF Alliance. We analyse SAR data in regard to changes in ice dynamics, volume and mass changes as well as glacier extent using SAR coherence. Our aim is to contribute to an improved system understanding merging the information terieved from earth observation with other data sources. For this purpose we develop algorithms based on data set from ALOS PALSAR and TerraSAR-X/TanDEM-X that provide respective products.
Project team
Saurabh Vijay, Melanie Rankl, Thorsten Seehaus, Matthias Braun
Full HGF-EDA Website
belspo
Funding period: 2016-2018
Project team: Hannes Feilhauer, Sandra Skowronek, and Iris Unberath
Species invasions are among the most important threats to the functioning of the Earth’s ecosystems. Invasion biologists have mainly focused so far on the effects that invasive plant species have on native populations and communities. The response of ecosystem functioning to invasion has received considerably less attention. In INPLANT we explore the capability of imaging spectroscopy data to define optically distinguishable functional types (‘optical types’) as a means to quantify the effects of invasive plants on ecosystem functioning. Spectroscopy data allow to characterize the canopy biochemistry, as such allowing a discrimination between subtle physiological differences among plant species, and enable a straightforward link to ecosystem processes. The optical types are expected to outperform, or at least complement, conventional functional trait approaches when predicting changes in ecosystem functioning through plant invasion. The principal idea behind INPLANT is that invasive plant species may have physical-chemical properties that differ from native species. These physical-chemical properties can be directly linked to ecosystem functioning changes following invasions, and they can be largely quantified based on the optical reflectance spectra of the species, which are detectable due to recent developments in remote sensing technology.
Project partners: KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium
Funding period: 2015 – 2017 (resp.)
This project devotes itself to the question, what is the change in height by the densification of firn.
The test area is the Vestfonna Ice Cap (VIC) on the island Nordaustlandet in the north east of Svalbard. The VIC is ~2400 km² in size and has a dome like shape with well defined outlet glaciers. Further test sites with a magnificent in situ measurement archive are welcome.
The propulsion are inaccuracies introduced during the conversion between measured volume change into glacier mass changes. Until now, we calculated glacier mass balances with a constant conversion factor of 850 kg m-3 or the density of ice (917 kg m-3) for entire glacier basins, altitude dependent density variations and firn layer thickness were unnoticed this way. Or we used constant densities for the ablation (900 kg m-3) and accumulation (600 kg m-3) areas, whereby not homogeneous density variations with varying climate conditions were not considered. A decline of the accuracy in the amount of mass change is the consequence. This inaccuracy is a systematic component of uncertainty in geodetically determined mass balances, and thus need to be addressed for accuracy improvement.
The aim is to develop a firn elevation change model (FecMo) Surface Energy Balance (SEB) parameters (e.g. radiation, temperature, wind speed, precipitation, cloud cover fraction). At the moment the model is based on the COupled Snowpack and Ice surface energy and MAss balance glacier model (COSIMA) developed by Huintjes et al. (2015) (link to the open access Git repository). Latter model consists of a SEB model and an integrated subsurface model. Beside the surface energy component, the model has a discrete layer based subsurface structure.
To remove access restrictions by proprietary software, COSIMA-FecMo is developed in the programming language Python. Simple configuration and site specific initialization options will be implemented, additionally it will be possible to replace entire Py-modules (e.g. precipitation, albedo, densification) if more accurate modules are available. The python model will be offered to the scientific community.
FecMo will be forced by climate reanalysis data (e.g. Modèle Atmosphérique Régional (MAR), ERA-interim data from the ECMWF). The forcing will be validated by a AWS network on and around the ice cap. One part of AWS data was recorded during the International Polar Year Project Kinnvika (IPY Kinnvika) between 2007 and 2010, another part is free of charge from the MET Norway (eKlima) and the UNIS. FecMo will be calibrated by in situ measurements from the IPY Kinnvika on mass balance components (ablation, snow package character, firn properties).
The project combines remote sensing data (TanDEM-X, ICESat, CryoSat-2, Sentinel-1A, Aster) and methods (DInSAR, geodetic approach), climate data reanalysis and downscaling (MAR/ERA-Interim) and the extensive analysis of the IPY Kinnvika archive (GPR, snow pit, stake and AWS measurements, GPS and DGPS profiles).
At the end of our study, we will be able to derive layer based firn densities and to estimate firn densification on glaciers and ice caps to retrieve the amount of elevation change that is attributed to compaction.
Project members: Björn Saß
Bibliography:
Huintjes E, Sauter T, Schröter B, et al (2015) Evaluation of a Coupled Snow and Energy Balance Model for Zhadang Glacier, Tibetan Plateau, Using Glaciological Measurements and Time-Lapse Photography. Arct Antarct Alp Res 47:573–590. doi: 10.1657/AAAR0014-073
This work is funded by the German Environmental Foundation Scholarship Program (Deutsche Bundesstiftung Umwelt, DBU).
Subproject in dt-chil. Verbund GABY-VASA: Responses of Glaciers, Biosphere and Hydrology to Climate Change and Climate change across the Southern Andes
Modelling present glacier dynamics on Svalbard – from inferring surface velocities to computing a flow-consistent bedrock map
Global surface temperatures have risen by ~0.7°C over the previous century. Due to an inherent amplification of climatic changes in high latitudes, warming has been more expressed in Polar Regions. One eminent consequence is the general retreat of Svalbard glaciers observed throughout the last century. In the last decades, southern Svalbard glaciers have even moved on to thin at dramatically increasing rates. This latest thinning trend is however not confirmed throughout the Arctic. The reason relies in the unique climatic conditions on Svalbard. 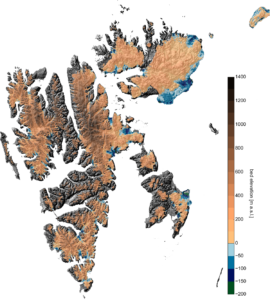 Since warm ocean currents in the North Atlantic reach the southern tip of the archipelago, the climate is rather warm and variable for its latitudinal band. Evolution of Svalbard glaciers has therefore often been suggested to play a precursor role for the other Arctic regions.Within the Arctic, Svalbard is unique in another respect, as glacier extents and elevation changes are well characterised over several decades. However, the interpretation of these geometric changes in terms of the climatic evolution is inhibited, as they arise from both the climatic surface mass balance and from ice flow divergence. The latter depends on glacier geometry and dynamics, and is not necessarily directly controlled by changes in climatological parameters. Yet, observations on glacier thicknesses and velocities are sparse and temporally incoherent, which impedes to this day a reliable quantification of the dynamic control on Svalbard glacier changes. By extension, we have only a vague idea on how much volume is annually discharged by iceberg calving at the marine ice fronts. Ice discharge presumably explains a large portion in the total mass budget, as more than half of the ice-covered area drains through marine-terminated glaciers.The aim of the research proposal is to expand the knowledge on the ice dynamic component of glacier evolution to the entire Svalbard archipelago. To this end, surface velocities are inferred from satellite remote sensing, which, in turn, serve to reconstruct the bedrock topography beneath all ice-covered areas. The reconstruction makes use of the mass conservation principle, provides therefore a flow-consistent thickness map and is already implemented in our ice flow model. Information on both ice velocities and ice thickness are a prerequisite to quantify the ice flow divergence that explains a, to this day, largely unknown portion of glacier changes. The reconstruction will therefore make it possible to better interpret recent geometric changes in the light of the observed atmospheric warming in the Arctic. Moreover, previous extrapolations for archipelago-wide estimates of ice volume and discharge can be improved on a physical basis. As the bedrock reconstruction is consistent with the observed ice flow, the map will facilitate the application of ice flow models on Svalbard. With our flow model, we aim at inferring the contribution of basal sliding to present glacier flow.
Since warm ocean currents in the North Atlantic reach the southern tip of the archipelago, the climate is rather warm and variable for its latitudinal band. Evolution of Svalbard glaciers has therefore often been suggested to play a precursor role for the other Arctic regions.Within the Arctic, Svalbard is unique in another respect, as glacier extents and elevation changes are well characterised over several decades. However, the interpretation of these geometric changes in terms of the climatic evolution is inhibited, as they arise from both the climatic surface mass balance and from ice flow divergence. The latter depends on glacier geometry and dynamics, and is not necessarily directly controlled by changes in climatological parameters. Yet, observations on glacier thicknesses and velocities are sparse and temporally incoherent, which impedes to this day a reliable quantification of the dynamic control on Svalbard glacier changes. By extension, we have only a vague idea on how much volume is annually discharged by iceberg calving at the marine ice fronts. Ice discharge presumably explains a large portion in the total mass budget, as more than half of the ice-covered area drains through marine-terminated glaciers.The aim of the research proposal is to expand the knowledge on the ice dynamic component of glacier evolution to the entire Svalbard archipelago. To this end, surface velocities are inferred from satellite remote sensing, which, in turn, serve to reconstruct the bedrock topography beneath all ice-covered areas. The reconstruction makes use of the mass conservation principle, provides therefore a flow-consistent thickness map and is already implemented in our ice flow model. Information on both ice velocities and ice thickness are a prerequisite to quantify the ice flow divergence that explains a, to this day, largely unknown portion of glacier changes. The reconstruction will therefore make it possible to better interpret recent geometric changes in the light of the observed atmospheric warming in the Arctic. Moreover, previous extrapolations for archipelago-wide estimates of ice volume and discharge can be improved on a physical basis. As the bedrock reconstruction is consistent with the observed ice flow, the map will facilitate the application of ice flow models on Svalbard. With our flow model, we aim at inferring the contribution of basal sliding to present glacier flow.
Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) – Projektnummer 274939856![]()
Remote Sensing of Mountain Glaciers
Assessment of essential climate variables to support international initiatives
– Development and refinement of methods, exemplarily applied in the tropical Andes
Methodenentwicklung und -verfeinerungen mit
GEKKO Gebirgsgletscher Essentielle Klimavariablen der KryOsphere
The glaciers of the tropical Andes represent an important water resource, but they are strongly affected by climate change. The regional water supply depends on the melt water and consequently on the mass balance of the glaciers. The goal of this project is to quantify glacier changes in the tropical Andes by analyzing different remote sensing data sets (SAR, optical imagery). Various glaciological variables (e.g., glacier extend, surface type, equilibrium line altitude, surface velocity) and their changes are going to be determined. Geodetic glacier mass balance is going to be derived from TanDEM-X and SRTM elevation models. New and upcoming Sensors like Sentinel-1&2 will be integrated in the analysis to estimate their capabilities for glacier monitoring. The results will provide essential information of the current state and ongoing changes of glaciers in the tropical Andes. An additional outcome is going to be a refined monitoring system for mountain glaciers.
Project team
Matthias Braun, Thorsten Seehaus
Founded by DLR & BMWI


IMProved gEodetiC glaCier mAss BaLancE measurements by integrating remote sensing, surface mass balance and firn compaction modelling – a case study from James Ross Island, Antarctica (IMPECCABLE)
Duration: 2016-2019
The aim of this project is an improvement of current estimates of glacier mass loss at James Ross island (JRI) on the east coast of the Antarctic Peninsula by comparing geodetic and flux approaches.
Glaciers draining into the ice shelves responded with flow acceleration and increased ice discharge to ice shelf disintegration (e.g. Larsen A/B) in the last years. There are still many uncertainties in mass balance modelling e.g. due to neglecting mass loss due to calving, unclear grounding line position, as well as errors in measured ice-thickness or conversion from volume to mass. Therefore, the differences between different models are not negligible and in situ measurements for validation are necessary.
This projects will try to overcome these limitations by the integration of the following measurements into the model creation:
-
In situ surface mass balance measurements, installation of two automatic weather stations and time lapse cameras on Gourdon Glacier
-
Static and kinematic differential as well as continuous GNSS measurements on JRI plateau and Gourdon Glacier
-
Ground Penetrating Radar surveys by helicopter
-
Elevation and volume change measurements by DinSAR
-
Ice dynamics from repeat TerraSAR-X acquisitions
Project-Members: Stefan Lippl, Prof. Dr. Matthias Braun
Project-Partners: Dr. Daniel Nyvlt, Dr. Kamil Laska, Dr. Zdenek Stachon (Masaryk University, Brno), Dr. Zbynek Engel (Carles University, Prague), Ing. Sebastian Marinsek (Instituto Antártico Argentino)
Founded by DFG under number BR2105/13-1 within the czech-german collaborative candidacy 2015
Tapping the potential of Earth Observations (TAPE) – FAU Emerging Fields Initiative
Project staff: Thorsten Seehaus, Lukas Sochor, Matthias Braun, Johannes Fürst, Eberhard Bänsch, Andreas Maier, Nora Gourmelon
The aim of this project is to analyse the time series of Earth observation (EO) data with innovative ‘deep learning’ methods in order to develop efficient algorithms for dealing with the large amounts of data involved. The value of these EO products is further increased by advanced interpolation techniques and assimilation in geophysical models from applied mathematics.
Funding period 2019-2022
Funded by FAU
Development of an interactive data portal for the processing and distribution of glaciological variables derived from Sentinel-1 data (for glaciers and ice caps outside of the polar ice sheets) (RETREAT)
Project staff: Matthias Braun, Thorsten Seehaus, Peter Friedl
Glaciers and ice caps are essential climate variables and a longterm monitoring of cryospheric changes is of high scientific and socio-economic interest. The Sentinel satellites of the European Copernicus Program provide a continues stream of remote sensing data covering glaciers and ice caps. The aims of this project are: To implement an automatic processing chain on CODE-DE to derive glacier flow speed and extent information from Sentinel data; to archive, visualize and provide the obtained products via an interactive user interface. By using intensity feature tracking, glacier flow speed fields are computed based on Sentinel-1 SAR image pairs. Glacier extent is mapped by analyzing the coherence pattern of repeat pass SAR acquisitions. Moreover, calibrated SAR intensity images as well as Sentinel-2 RGB composites are also included in the database. Additionally, glaciological datasets (e.g. glacier inventories, altimeter data, digital elevation models) from different sources (external and from the work group) will be included and visualized in the database in order to support the online analysis of glaciological changes. The goal is to establish an interactive glaciological data portal for a broad spectrum (science, education, media, politics) of users.
Funding period 2018-2020
Funded by BMWK
Past, present and future glacier evolution in the Tropical Andes (PPF-TA)
Project staff: Thorsten Seehaus
Initial funding by FAU Emerging Talents Initiative for project preparation.
Within the project, the aerial imagery archive of Prof. E. Jordan was transferred to FAU, widely digitized and a precursor study was conducted.
Funding period 2021-2022
Funded by FAU Emerging Talents Initiative
2024
- , :
Mit dem Polarflugzeug über Patagonien
In: Geographische Rundschau 76 (2024), S. 57-
ISSN: 0016-7460
BibTeX: Download - , :
Mit dem Polarflugzeug über Patagonien
In: Geographische Rundschau 76 (2024), S. 57
ISSN: 0016-7460
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , :
The foundations of the Patagonian icefields
In: Communications Earth & Environment 5 (2024), Art.Nr.: 142
ISSN: 2662-4435
DOI: 10.1038/s43247-023-01193-7
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , :
Assessing supraglacial lake depth using ICESat-2, Sentinel-2, TanDEM-X, and in situ sonar measurements over Northeast and Southwest Greenland
In: Cryosphere 18 (2024), S. 5431-5449
ISSN: 1994-0416
DOI: 10.5194/tc-18-5431-2024
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , :
Observing glacier elevation changes from spaceborne optical and radar sensors - an inter-comparison experiment using ASTER and TanDEM-X data
In: Cryosphere 18 (2024), S. 3195-3230
ISSN: 1994-0416
DOI: 10.5194/tc-18-3195-2024
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , :
Velocity variations and hydrological drainage at Baltoro Glacier, Pakistan
In: Cryosphere 18 (2024), S. 1085-1103
ISSN: 1994-0416
DOI: 10.5194/tc-18-1085-2024
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , :
Contextual HookFormer for Glacier Calving Front Segmentation
In: IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 62 (2024), S. 1-15
ISSN: 0196-2892
DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2024.3368215
URL: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10440599
BibTeX: Download
2023
- , , , , , , , , , , , , , :
Big data in Antarctic sciences-current status, gaps, and future perspectives
In: Polarforschung 91 (2023), S. 45-57
ISSN: 0032-2490
DOI: 10.5194/polf-91-45-2023
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , :
Out-of-the-box Calving Front Detection Method Using Deep Learning
In: Cryosphere 17 (2023), S. 4957–4977
ISSN: 1994-0416
DOI: 10.5194/tc-17-4957-2023
BibTeX: Download - , , , :
Automated Detection of Glacier Surges from Sentinel-1 Surface Velocity Time Series-An Example from Svalbard
In: Remote Sensing 15 (2023)
ISSN: 2072-4292
DOI: 10.3390/rs15061545
BibTeX: Download - , , , :
Mass changes of the northern Antarctic Peninsula Ice Sheet derived from repeat bi-static synthetic aperture radar acquisitions for the period 2013–2017
In: Cryosphere 17 (2023), S. 4629-4644
ISSN: 1994-0416
DOI: 10.5194/tc-17-4629-2023
BibTeX: Download - , , , , :
Estimating ice discharge of the Antarctic Peninsula using different ice-thickness datasets
In: Annals of Glaciology (2023), S. 1-12
ISSN: 0260-3055
DOI: 10.1017/aog.2023.67
BibTeX: Download - , , , :
Constraining regional glacier reconstructions using past ice thickness of deglaciating areas - a case study in the European Alps
In: Cryosphere 17 (2023), S. 2285-2303
ISSN: 1994-0416
DOI: 10.5194/tc-17-2285-2023
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , , :
Strategies for regional modeling of surface mass balance at the Monte Sarmiento Massif, Tierra del Fuego
In: Cryosphere 17 (2023), S. 2343--2365
ISSN: 1994-0416
DOI: 10.5194/tc-17-2343-2023
URL: https://tc.copernicus.org/articles/17/2343/2023/
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , :
AMD-HookNet for Glacier Front Segmentation
In: IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 61 (2023), S. 1-12
ISSN: 0196-2892
DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3245419
URL: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10044700
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , :
Insights into German polar research during POLARSTUNDE
In: Polarforschung 91 (2023), S. 73-80
ISSN: 0032-2490
DOI: 10.5194/polf-91-73-2023
BibTeX: Download
2022
- , , , , , :
Pixel-wise Distance Regression for Glacier Calving Front Detection and Segmentation
In: IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 60 (2022), S. 1-10
ISSN: 0196-2892
DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2022.3158591
URL: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.05715
BibTeX: Download - , , , , :
Calving fronts and where to find them: a benchmark dataset and methodology for automatic glacier calving front extraction from synthetic aperture radar imagery
In: Earth System Science Data 14 (2022), S. 4287--4313
ISSN: 1866-3508
DOI: 10.5194/essd-14-4287-2022
URL: https://essd.copernicus.org/articles/14/4287/2022/
BibTeX: Download - , , , , :
Glacier inventory and recent variations of Santa Inés Icefield, Southern Patagonia
In: Arctic, Antarctic, and Alpine Research 54 (2022), S. 202-220
ISSN: 1523-0430
DOI: 10.1080/15230430.2022.2071793
BibTeX: Download - , , :
The West Kunlun Glacier Anomaly and Its Response to Climate Forcing during 2002–2020
In: Remote Sensing 14 (2022), S. 3465
ISSN: 2072-4292
DOI: 10.3390/rs14143465
BibTeX: Download - , , , , :
A Self-Trained Model for Cloud, Shadow and Snow Detection in Sentinel-2 Images of Snow- and Ice-Covered Regions
In: Remote Sensing 14 (2022), S. 1825
ISSN: 2072-4292
DOI: 10.3390/rs14081825
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , :
How to Get the Most Out of U-Net for Glacier Calving Front Segmentation
In: IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing (2022)
ISSN: 1939-1404
DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3148033
BibTeX: Download - , , , :
Brief communication: Increased glacier mass loss in the Russian High Arctic (2010-2017)
In: Cryosphere 16 (2022), S. 35-42
ISSN: 1994-0416
DOI: 10.5194/tc-16-35-2022
BibTeX: Download
2021
- , , , , , , :
On Mathews Correlation Coefficient and Improved Distance Map Loss for Automatic Glacier Calving Front Segmentation in SAR Imagery
In: IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing (2021), S. 1-12
ISSN: 0196-2892
DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3115883
URL: https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.08312
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , :
Acceleration of Dynamic Ice Loss in Antarctica From Satellite Gravimetry
In: Frontiers in Earth Science 9 (2021)
ISSN: 2296-6463
DOI: 10.3389/feart.2021.741789
BibTeX: Download - , , , , :
Using floristic gradient mapping to assess seasonal thaw depth in interior Alaska
In: Applied Vegetation Science 24 (2021), Art.Nr.: e12561
ISSN: 1654-109X
DOI: 10.1111/avsc.12561
BibTeX: Download - , , :
Global time series and temporal mosaics of glacier surface velocities derived from Sentinel-1 data
In: Earth System Science Data 13 (2021), S. 4653-4675
ISSN: 1866-3508
DOI: 10.5194/essd-13-4653-2021
BibTeX: Download - , , , , :
Fully Automated Detection of Supraglacial Lake Area for Northeast Greenland Using Sentinel-2 Time-Series
In: Remote Sensing 13 (2021), S. 205
ISSN: 2072-4292
DOI: 10.3390/rs13020205
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , , , :
Distributed Global Debris Thickness Estimates Reveal Debris Significantly Impacts Glacier Mass Balance
In: Geophysical Research Letters 48 (2021), Art.Nr.: e2020GL091311
ISSN: 0094-8276
DOI: 10.1029/2020GL091311
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , :
Der Arbeitskreis "polargeodäsie und Glaziologie"
In: Polarforschung 89 (2021), S. 57-64
ISSN: 0032-2490
DOI: 10.5194/polf-89-57-2021
BibTeX: Download - , , , , :
Geodetic Mass Balance of the South Shetland Islands Ice Caps, Antarctica, from Differencing TanDEM-X DEMs
In: Remote Sensing 13 (2021), S. 3408
ISSN: 2072-4292
DOI: 10.3390/rs13173408
BibTeX: Download - , , :
Increased Ice Thinning over Svalbard measured by ICESat/ICESat-2 Laser Altimetry
In: Remote Sensing 13 (2021), Art.Nr.: 2089
ISSN: 2072-4292
DOI: 10.3390/rs13112089
URL: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-4292/13/11/2089
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , :
Subglacial discharge controls seasonal variations in the thermal structure of a glacial lake in Patagonia
In: Nature Communications 12 (2021), Art.Nr.: 6301
ISSN: 2041-1723
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-26578-0
BibTeX: Download - , , , :
Observational Assessments of Glacier Mass Changes at Regional and Global Level
In: Frontiers in Earth Science 8 (2021), Art.Nr.: 641710
ISSN: 2296-6463
DOI: 10.3389/feart.2020.641710
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , , , :
Measuring and inferring the ice thickness distribution of four glaciers in the Tien Shan, Kyrgyzstan
In: Journal of Glaciology 67 (2021), S. 269-286
ISSN: 0022-1430
DOI: 10.1017/jog.2020.104
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , :
Seasonal Evolution of Supraglacial Lakes on Baltoro Glacier From 2016 to 2020
In: Frontiers in Earth Science 9 (2021)
ISSN: 2296-6463
DOI: 10.3389/feart.2021.725394
BibTeX: Download
2020
- , , , , , :
Glacier runoff variations since 1955 in the Maipo River basin, in the semiarid Andes of central Chile
In: Cryosphere 14 (2020), S. 2005-2027
ISSN: 1994-0416
DOI: 10.5194/tc-14-2005-2020
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , , :
60 years of glacier elevation and mass changes in the Maipo River Basin, central Andes of Chile
In: Remote Sensing 12 (2020), Art.Nr.: 1658
ISSN: 2072-4292
DOI: 10.3390/rs12101658
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , , :
Detailed quantification of glacier elevation and mass changes in South Georgia
In: Environmental Research Letters (2020)
ISSN: 1748-9326
DOI: 10.1088/1748-9326/ab6b32
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , , , , , , :
A near 90-year record of the evolution of El Morado Glacier and its proglacial lake, Central Chilean Andes
In: Journal of Glaciology 66 (2020), S. 846-860
ISSN: 0022-1430
DOI: 10.1017/jog.2020.52
BibTeX: Download - , , , :
Remote sensing of glacier and ice sheet grounding lines: A review
In: Earth-Science Reviews 184 (2020)
ISSN: 0012-8252
DOI: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.102948
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , :
Uncertainty Assessment of Ice Discharge Using GPR-Derived Ice Thickness from Gourdon Glacier, Antarctic Peninsula
In: Geosciences 10 (2020), S. 12
ISSN: 2076-3263
DOI: 10.3390/geosciences10010012
URL: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3263/10/1/12
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , :
Perito Moreno Glacier dam rupture - A recurrent natural experiment to probe solid-earth elasticity
In: Journal of South American Earth Sciences 104 (2020), Art.Nr.: 102904
ISSN: 0895-9811
DOI: 10.1016/j.jsames.2020.102904
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , :
A tree-ring delta O-18 series from southernmost Fuego-Patagonia is recording flavors of the Antarctic Oscillation
In: Global and Planetary Change 195 (2020)
ISSN: 0921-8181
DOI: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2020.103302
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , :
Hydrological development and phenology of lakes of the fildes peninsula – Antarctica Desenvolvimento hidrológico e fenologia de lagos da península fildes – Antártica
In: Geociencias 39 (2020), S. 559-572
ISSN: 0101-9082
DOI: 10.5016/geociencias.v39i2.14453
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , :
The effects of climatic change on glacial, proglacial and paraglacial systems at Collins Glacier, King George Island, Antarctica, from the end of the little ice age to the 21st century Los efectos de los cambios climáticos en los sistemas glaciales, proglaciales y periglaciales del glaciar Collins, isla Rey Jorge, Antártica, del final de la Pequeña Edad del Hielo al siglo XXI
In: Investigaciones Geográficas (2020), Art.Nr.: e60153
ISSN: 0188-4611
DOI: 10.14350/RIG.60153
BibTeX: Download - , , , :
Surface energy fluxes on Chilean glaciers: measurements and models
In: Cryosphere 14 (2020), S. 2545-2565
ISSN: 1994-0416
DOI: 10.5194/tc-14-2545-2020
BibTeX: Download - , , , , :
Editorial: Climate Impacts on Glaciers and Biosphere in Fuego-Patagonia
In: Frontiers in Earth Science 8 (2020), Art.Nr.: 91
ISSN: 2296-6463
DOI: 10.3389/feart.2020.00091
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , :
Mass balance and area changes of glaciers in the Cordillera Real and Tres Cruces, Bolivia, between 2000 and 2016
In: Journal of Glaciology (2020), S. 1-13
ISSN: 0022-1430
DOI: 10.1017/jog.2019.94
BibTeX: Download - , , , , :
Novel Techniques for Void Filling in Glacier Elevation Change Data Sets
In: Remote Sensing 12 (2020), S. 3917
ISSN: 2072-4292
DOI: 10.3390/rs12233917
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , :
Spatial and temporal analysis of changes in the glaciers of the Antarctic Peninsula
In: Global and Planetary Change 184 (2020), Art.Nr.: 103079
ISSN: 0921-8181
DOI: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2019.103079
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , :
Rapid glacier retreat and downwasting throughout the European Alps in the early 21st century
In: Nature Communications 11 (2020), Art.Nr.: 3209
ISSN: 2041-1723
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-16818-0
BibTeX: Download - , , , :
Brief communication: Glacier thickness reconstruction on Mt. Kilimanjaro
In: Cryosphere 14 (2020), S. 3399-3406
ISSN: 1994-0416
DOI: 10.5194/tc-14-3399-2020
BibTeX: Download
2019
- , , , , , , , , :
Constraining glacier elevation and mass changes in South America
In: Nature Climate Change 9 (2019), S. 130–136
ISSN: 1758-678X
DOI: 10.1038/s41558-018-0375-7
URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41558-018-0375-7?WT.feed_name=subjects_climate-sciences
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , :
Assessing Snow Accumulation Patterns and Changes on the Patagonian Icefields
In: Frontiers in Environmental Science 7 (2019)
ISSN: 2296-665X
DOI: 10.3389/fenvs.2019.00030
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , :
Interannual variability in glacier contribution to runoff from a high-elevation Andean catchment: understanding the role of debris cover in glacier hydrology
In: Hydrological Processes 33 (2019), S. 214-229
ISSN: 0885-6087
DOI: 10.1002/hyp.13354
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , :
Geodetic Mass Balances and Area Changes of Echaurren Norte Glacier (Central Andes, Chile) between 1955 and 2015
In: Remote Sensing 11 (2019)
ISSN: 2072-4292
DOI: 10.3390/rs11030260
URL: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-4292/11/3/260
BibTeX: Download - , , , , :
Remotely sensed estimation of vegetation shifts in the polar and alpine tree-line ecotone in Finnish Lapland during the last three decades
In: Forest Ecology and Management 454 (2019), Art.Nr.: 117668
ISSN: 0378-1127
DOI: 10.1016/j.foreco.2019.117668
BibTeX: Download - , , , :
Remote sensing of glacier and ice sheet grounding lines: A review
In: Earth-Science Reviews (2019)
ISSN: 0012-8252
DOI: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.102948
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , :
Spatial and Temporal Variability of Glacier Surface Velocities and Outlet Areas on James Ross Island, Northern Antarctic Peninsula.
In: Geosciences 9 (2019), S. 1-34
ISSN: 2076-3263
DOI: 10.3390/geosciences9090374
URL: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3263/9/9/374
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , :
Late Holocene Glacial Fluctuations of Schiaparelli Glacier at Monte Sarmiento Massif, Tierra del Fuego (54 degrees 24 ' S)
In: Geosciences 9 (2019)
ISSN: 2076-3263
DOI: 10.3390/geosciences9080340
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , :
Changes of the tropical glaciers throughout Peru between 2000 and 2016 - Mass balance and area fluctuations
In: Cryosphere 13 (2019), S. 2537-2556
ISSN: 1994-0416
DOI: 10.5194/tc-13-2537-2019
BibTeX: Download
2018
- , , , , , , , :
Estimating surface melt and runoff on the Antarctic Peninsula using ERA-Interim reanalysis data
In: Antarctic Science 30 (2018), S. 379-393
ISSN: 0954-1020
DOI: 10.1017/S0954102018000391
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , , , , , , , :
LiDAR derived forest structure data improves predictions of canopy N and P concentrations from imaging spectroscopy.
In: Remote Sensing of Environment 211 (2018), S. 13-25
ISSN: 0034-4257
DOI: 10.1016/j.rse.2018.03.038
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , :
Analyzing remotely sensed structural and chemical canopy traits of a forest invaded by Prunus serotina over multiple spatial scales.
In: Biological Invasions 8 (2018), S. 2257-2271
ISSN: 1573-1464
DOI: 10.1007/s10530-018-1700-9
BibTeX: Download - , , , , :
Are remotely-sensed traits suitable for ecological analysis? A case study of long-term drought effects on Leaf Mass per Area of wetland vegetation
In: Ecological Indicators 88 (2018), S. 232-240
ISSN: 1470-160X
DOI: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.01.012
BibTeX: Download - , , , , :
Recent dynamic changes on Fleming Glacier after the disintegration of Wordie Ice Shelf, Antarctic Peninsula
In: Cryosphere (2018)
ISSN: 1994-0416
DOI: 10.5194/tc-12-1347-2018
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , :
The ice‐free topography of Svalbard
In: Geophysical Research Letters 45 (2018), S. 11760-11769
ISSN: 0094-8276
DOI: 10.1029/2018GL079734
URL: https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/action/showCitFormats?doi=10.1029/2018GL079734
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , , :
Imprints of climate signals in a 204 year δ18O tree-ring record of nothofagus pumilio from Perito Moreno Glacier, Southern Patagonia (50◦S)
In: Frontiers in Earth Science 6 (2018), Art.Nr.: 27
ISSN: 2296-6463
DOI: 10.3389/feart.2018.00027
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , , , :
Glacier protection laws: Potential conflicts in managing glacial hazards and adapting to climate change
In: Ambio 47 (2018), S. 835-845
ISSN: 0044-7447
DOI: 10.1007/s13280-018-1043-x
URL: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13280-018-1043-x
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , :
Benthic meltwater fjord habitats formed by rapid glacier recession on King George Island, Antarctica
In: Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A-Mathematical Physical and Engineering Sciences (2018)
ISSN: 1364-503X
DOI: 10.1098/rsta.2017.0178
BibTeX: Download - , , :
Automatic delineation of debris-covered glaciers using InSAR coherence derived from X-, C- and L-band radar data: a case study of Yazgyl Glacier
In: Journal of Glaciology 64 (2018), S. 1–11
ISSN: 0022-1430
DOI: 10.1017/jog.2018.70
URL: https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/journal-of-glaciology/article/automatic-delineation-of-debriscovered-glaciers-using-insar-coherence-derived-from-x-c-and-lband-radar-data-a-case-study-of-yazgyl-glacier/CA054F73D1CDEB11C1F6491D71583066
BibTeX: Download - , , , , :
Mapping plant functional groups in subalpine grassland of the Greater Caucasus
In: Mountain Research and Development 38 (2018), S. 63-72
ISSN: 0276-4741
DOI: 10.1659/mrd-journal-d-17-00082.1
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , :
Elevation and mass changes of the southern Patagonia icefield derived from TanDEM-X and SRTM data
In: Remote Sensing 10 (2018), Art.Nr.: 188
ISSN: 2072-4292
DOI: 10.3390/rs10020188
URL: http://www.mdpi.com/2072-4292/10/2/188
BibTeX: Download - , , , :
An updated multi-temporal glacier inventory for the Patagonian Andes with changes between the Little Ice Age and 2016
In: Frontiers in Earth Science 6 (2018), Art.Nr.: 62
ISSN: 2296-6463
DOI: 10.3389/feart.2018.00062
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , :
Remotely sensed spatial heterogeneity as an exploratory tool for taxonomic and functional diversity studies.
In: Ecological Indicators 85 (2018), S. 983-990
ISSN: 1470-160X
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , :
Measuring β-diversity by remote sensing: a challenge for biodiversity monitoring.
In: Methods in Ecology and Evolution 9 (2018), S. 1787-1798
ISSN: 2041-210X
DOI: 10.1111/2041-210x.12941
BibTeX: Download - , , , :
Changes in glacier dynamics in the northern Antarctic Peninsula since 1985
In: Cryosphere 12 (2018), S. 577-594
ISSN: 1994-0416
DOI: 10.5194/tc-12-577-2018
BibTeX: Download - , :
Early 21st century spatially detailed elevation changes of Jammu and Kashmir glaciers (Karakoram–Himalaya)
In: Global and Planetary Change 165 (2018), S. 137-146
ISSN: 0921-8181
DOI: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2018.03.014
BibTeX: Download
2017
- , :
Seasonal and interannual variability of Columbia Glacier, Alaska (2011-2016): Ice Velocity, Mass Flux, surface elevation and front position
In: Remote Sensing 9 (2017), Art.Nr.: 635
ISSN: 2072-4292
DOI: 10.3390/rs9060635
BibTeX: Download - , , :
Optical trait indicators for remote sensing of plant species composition: predictive power and seasonal variability
In: Ecological Indicators 73 (2017), S. 825-833
ISSN: 1470-160X
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , , , , , , , :
Application of a two-step approach for mapping ice thickness to various glacier types on Svalbard
In: Cryosphere 11 (2017), S. 2003-2032
ISSN: 1994-0416
DOI: 10.5194/tc-11-2003-2017
BibTeX: Download - , , , :
Dynamic changes on the Wilkins Ice Shelf during the 2006-2009 retreat derived from satellite observations
In: Cryosphere 11 (2017), S. 1199-1211
ISSN: 1994-0416
DOI: 10.5194/tc-11-1199-2017
BibTeX: Download - , , , :
Glacier changes in the Susitna Basin, Alaska, USA, (1951-2015) using GIS and remote sensing methods
In: Remote Sensing 9 (2017), Art.Nr.: 85
ISSN: 2072-4292
DOI: 10.3390/rs9050478
BibTeX: Download
2016
- , :
Elevation change rates of glaciers in the Lahaul-Spiti (Western Himalaya, India) during 2000-2012 and 2012-2013
In: Remote Sensing 8 (2016), Art.Nr.: 1038
ISSN: 2072-4292
DOI: 10.3390/rs8121038
BibTeX: Download - , , , :
Monitoring snow and ice surfaces on King George Island, Antarctic Peninsula, with high-resolution TerraSAR-X time series
In: Antarctic Science 28 (2016), S. 135-149
ISSN: 0954-1020
DOI: 10.1017/S0954102015000577
URL: http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=10200178&fileId=S0954102015000577
BibTeX: Download - , , , :
Mapping pollination types with remote sensing
In: Journal of Vegetation Science 27 (2016), S. 999-1011
ISSN: 1100-9233
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , :
The safety band of Antarctic ice shelves
In: Nature Climate Change 6 (2016), S. 479-482
ISSN: 1758-678X
DOI: 10.1038/nclimate2912
URL: http://www.nature.com/nclimate/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/nclimate2912.html
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , :
Linking earth observation and taxonomic, structural and functional biodiversity: local to ecosystem perspectives
In: Ecological Indicators 70 (2016), S. 317-339
ISSN: 1470-160X
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , :
Mapping raised bogs with an iterative one-class classification approach
In: Isprs Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 120 (2016), S. 53-64
ISSN: 0924-2716
BibTeX: Download - , :
Glacier elevation and mass changes over the central Karakoram region estimated from TanDEM-X and SRTM/X-SAR digital elevation models
In: Annals of Glaciology 51 (2016), S. 273-281
ISSN: 0260-3055
DOI: 10.3189/2016AoG71A024
URL: http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/igsoc/agl/pre-prints/content-ings_agl_71a024
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , :
Dynamic response of Sjögren inlet glaciers, Antarctic Peninsula, to ice shelf breakup derived from multi-mission remote sensing time series
In: Frontiers of Earth Science 4 (2016), Art.Nr.: 66
ISSN: 2095-0195
DOI: 10.3389/feart.2016.00066
BibTeX: Download - , , , :
Robust Change Vector Analysis (RCVA) for multi-sensor very high resolution optical satellite data.
In: International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 50 (2016), S. 131-140
ISSN: 1569-8432
BibTeX: Download - , , , , :
Estimating vegetation cover from high-resolution satellite data to assess grassland degradation in the Georgian Caucasus
In: Mountain Research and Development 36 (2016), S. 56-65
ISSN: 0276-4741
DOI: 10.1659/MRD-JOURNAL-D-15-00064.1
BibTeX: Download
2015
- , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , :
Earth and space observation at the German Antarctic Receiving Station O'Higgins
In: Polar Record 51 (2015), S. 590-610
ISSN: 0032-2474
DOI: 10.1017/S0032247414000540
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , :
Earth observation in Antarctica – the German Antarctic Receiving Station GARS Oiggins
In: Polar Record 51 (2015), S. 590-610
ISSN: 0032-2474
DOI: 10.1017/S0032247414000540
BibTeX: Download - , , , , :
Changes in ice dynamics, elevation and mass discharge of Dinsmoor-Bombardier-Edgeworth glacier system, Antarctic Peninsula
In: Earth and Planetary Science Letters 427 (2015), S. 125-135
ISSN: 0012-821X
DOI: 10.1016/j.epsl.2015.06.047
BibTeX: Download
2014
- , , , , :
Surface velocity and mass balance of Livingston Island ice cap, Antarctica
In: Cryosphere 8 (2014), S. 1807-1823
ISSN: 1994-0416
DOI: 10.5194/tc-8-1807-2014
URL: http://www.the-cryosphere.net/8/1807/2014/
BibTeX: Download - , , :
Glacier changes in the Karakoram region mapped by multimission satellite imagery
In: Cryosphere 8 (2014), S. 977-989
ISSN: 1994-0416
DOI: 10.5194/tc-8-977-2014
BibTeX: Download
2013
- , , , , :
Variability of the climatic mass balance of Vestfonna ice cap, northeastern Svalbard, 1979-2011
In: Annals of Glaciology 54 (2013), S. 254-264
ISSN: 0260-3055
DOI: 10.3189/2013AoG63A407
BibTeX: Download - , , , , :
Variability of the climatic mass balance of Vestfonna ice cap (northeastern Svalbard) in the period 1979/1980 – 2010/2011
In: Annals of Glaciology 54 (2013), S. 254-264
ISSN: 0260-3055
BibTeX: Download - , , , :
Surface velocity and ice discharge of the ice cap on King George Island, Antarctica
In: Annals of Glaciology 54 (2013), S. 111-119
ISSN: 0260-3055
DOI: 10.3189/2013AoG63A517
BibTeX: Download
2012
- , , , :
Surge dynamics on Bering Glacier, Alaska, in 2008–2011
In: Cryosphere 6 (2012), S. 1251-1262
ISSN: 1994-0416
DOI: 10.5194/tc-6-1251-2012
BibTeX: Download - , , :
Glacial transport of human waste and survival of fecal bacteria on Mt. McKinley's Kahiltna glacier, Denali National Park, Alaska
In: Arctic, Antarctic, and Alpine Research 44 (2012), S. 432-445
ISSN: 1523-0430
DOI: 10.1657/1938-4246-44.4.432
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , , , , :
Using surface velocities to calculate ice thickness and bed topography: A case study at Columbia Glacier, Alaska, USA
In: Journal of Glaciology 58 (2012), S. 1151-1164
ISSN: 0022-1430
DOI: 10.3189/2012JoG11J249
BibTeX: Download
2011
- Braun Matthias, Pohjola V. A., Pettersson R, Moeller M., Finkelnburg R., Falk U., Scherer D., Schneider C.:
Glacier frontal position changes of Vestfonna (Nordaustlandet, Svalbard)
In: Geografiska Annaler Series A-Physical Geography (2011), S. -
ISSN: 0435-3676
DOI: 10.1111/j.1468-0459.2011.00437.x
BibTeX: Download - Schneider C., Scherer D., Braun M.:
Impact of climate change on the cryosphere of the polar regions Auswirkungen des Klimawandels auf die Kryosphäre in den Polargebieten
In: Geographische Rundschau 63 (2011), S. 12-19
ISSN: 0016-7460
URL: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?partnerID=HzOxMe3b&scp=83755196723&origin=inward
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , , , :
Snowpack characteristics of Vestfonna and De Geerfonna (Nordaustlandet, Svalbard) - a spatiotemporal analysis based on multiyear snow-pit data
In: Geografiska Annaler Series A-Physical Geography 93 (2011), S. 273-285
ISSN: 0435-3676
DOI: 10.1111/j.1468-0459.2011.00440.x
BibTeX: Download - , , , , :
Karakoram glacier surge dynamics
In: Geophysical Research Letters 38 (2011)
ISSN: 0094-8276
DOI: 10.1029/2011GL049004
BibTeX: Download - , , , :
Observed glacial changes on the King George Island ice cap, Antarctica, in the last decade
In: Global and Planetary Change 79 (2011), S. 99-109
ISSN: 0921-8181
DOI: 10.1016/j.gloplacha
URL: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921818111001111
BibTeX: Download - , , :
Auswirkungen des Klimawandels auf die Kryosphäre in den Polargebieten
In: Geographische Rundschau 12 (2011), S. -
ISSN: 0016-7460
BibTeX: Download
2010
- Rückkamp M., Blindow N., Suckro S., Braun Matthias, Humbert A.:
Dynamics of the ice cap on King George Island, Antarctica - field measurements and numerical simulations
In: Annals of Glaciology 55 (2010), S. 80-90
ISSN: 0260-3055
DOI: 10.3189/172756410791392817
BibTeX: Download - Blindow N., Suckro S., Rückamp M., Braun Matthias, Schindler M., Breuer B., Saurer H., Simoes J. C., Lange S.:
Geometry and status of the King Georg Island ice cap, South Shetland Islands, Antarctica
In: Annals of Glaciology 55 (2010), S. 103-109
ISSN: 0260-3055
BibTeX: Download - Kurtz D., Schellberg J., Braun Matthias:
Ground and Satellite Based Assessment of Rangeland Management in Sub-Tropical Argentina
In: Applied Geography 30 (2010), S. 210-220
ISSN: 0143-6228
DOI: 10.1016/j.apgeog.2009.01.006
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , , , :
Deformation and failure of the ice bridge on Wilkins Ice Shelf, Antarctica
In: Annals of Glaciology 55 (2010), S. 49-55
ISSN: 0260-3055
DOI: 10.3189/172756410791392709
BibTeX: Download
2009
- , :
Recent retreat of Wilkins Ice Shelf reveals new insights in ice shelf break-up mechanisms
In: IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 2 (2009), S. 263-267
ISSN: 1545-598X
DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2008.2011925
BibTeX: Download - , , :
Changes of Wilkins Ice Shelf over the past 15 years and inferences on its stability
In: Cryosphere (2009), S. 41-56
ISSN: 1994-0416
DOI: 10.5194/tc-3-41-2009
URL: http://www.the-cryosphere.net/3/41/2009/tc-3-41-2009.html
BibTeX: Download - , :
Classifier ensembles for land cover mapping with multi-spectral SAR imagery
In: Isprs Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 5 (2009), S. 450-457
ISSN: 0924-2716
DOI: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2009.01.003
URL: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0924271609000070
BibTeX: Download
2008
- , :
Wilkins Ice Shelf break-up along failure zones
In: Journal of Glaciology 188 (2008), S. 943-944
ISSN: 0022-1430
BibTeX: Download - , , , , :
Precision agriculture on grassland: applications, perspectives and constraints a review
In: European Journal of Agronomy 29 (2008), S. 59-71
ISSN: 1161-0301
DOI: 10.1016/j.eja.2008.05.005
BibTeX: Download
2007
- Waske B., Braun Matthias, Menz G.:
An object-based speckle filter using multi-sensor remote sensing imagery
In: IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 2 (2007), S. 231-235
ISSN: 1545-598X
BibTeX: Download - , , :
Field observations on spatial variability of surface hoar at the basin scale
In: Journal of Geophysical Research F: Earth Surface 112 (2007), S. -
ISSN: 0148-0227
DOI: 10.1029/2006JF000587
BibTeX: Download
2006
- Over M., Siegmund A., Braun Matthias, Menz G.:
Monitoring of Land-use and Land-cover in North Rhine-Westphalia by Remote Sensing
In: Geographische Rundschau International Edition 1 (2006), S. 50-55
ISSN: 1860-7098
BibTeX: Download - , , , , , :
Firn layer impact on glacial runoff: a case study at Hofsjökull, Iceland
In: Hydrological Processes 20 (2006), S. 2171-2185
ISSN: 0885-6087
DOI: 10.1002/hyp.6201
BibTeX: Download
2005
- Schuler T., Hock J. M. , Elvehoy H., Braun Matthias, Brown I., Hagen J.-O.:
Distributed mass balance modelling on Engabreen (Norway)
In: Annals of Glaciology 42 (2005), S. 395-401
ISSN: 0260-3055
BibTeX: Download - Siebert S., Döll P., Hoogeveen J., Faures J.-M. , Frenken K., Feick Sebastian:
Development and validation of the global map of irrigation areas.
In: Hydrology and Earth System Sciences 9 (2005), S. 535-547
ISSN: 1027-5606
Open Access: http://www.hydrol-earth-syst-sci.net/9/535/2005/
BibTeX: Download
2004
- Weissteiner C., Braun Matthias, Kühlbauch W.:
Synergetic use of remote sensing and soilborne data for regional yield prediction of malting barley (Hordeum vulgare L.)
In: EARSeL eProceedings 3 (2004), S. 347-353
ISSN: 1729-3782
BibTeX: Download
2002
- Braun Matthias, Simoes J. C., Vogt S., Bremer U.F., Saurer H., Aquino F.E.:
A new satellite image map of King George Island (South Shetland Islands, Antarctica)
In: Polarforschung 71 (2002), S. 47-48
ISSN: 0032-2490
BibTeX: Download - Rau F., Braun Matthias:
The regional distribution of the dry snow zone on the Antarctic Peninsula north of 70°S
In: Annals of Glaciology 34 (2002), S. 95-100
ISSN: 0260-3055
BibTeX: Download
2001
- Rau F., Braun Matthias, Friedrich M., Weber F., Goßmann H.:
Radar glacier zones and their boundaries as indicators of glacier mass balance and climatic variability
In: EARSeL eProceedings 1 (2001), S. 317-327
ISSN: 1729-3782
BibTeX: Download - Braun Matthias, Saurer H., Vogt S., Simoes J. C., Goßmann H.:
The influence of large-scale circulation on surface energy balance on the King George Island ice cap
In: International Journal of Climatology 1 (2001), S. 21-36
ISSN: 0899-8418
BibTeX: Download
2000
- Braun Matthias, Schneider C.:
Characteristics of summertime energy balance along the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula
In: Annals of Glaciology (2000), S. 179-183
ISSN: 0260-3055
BibTeX: Download - Braun Matthias, Rau F., Saurer H., Goßmann:
Development of radar glacier zones on the King George Island ice cap, Antarctica, during the austral summer 1996/97 as observed by ERS2 SAR data
In: Annals of Glaciology (2000), S. 357-363
ISSN: 0260-3055
BibTeX: Download - Rau F., Braun Matthias, Saurer H., Goßmann H., Kothe G., Weber F., Wunderle S., Ebel M., Beppler D.:
Monitoring multi-year snow cover dynamics on the Antarctic Peninsula
In: Polarforschung 1/2 (2000), S. 27-40
ISSN: 0032-2490
BibTeX: Download